
Stevia: Market Trends & Economic Insights (2025)
The global Stevia market is shifting from a niche to a technology-driven segment of the sweetener industry, fueled by health trends, supportive regulations, and innovations addressing past product limitations. Reconciling various forecasts suggests a valuation of about USD 1.0 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 8–10% from 2025.
Growth is driven by rising obesity and diabetes rates, pushing demand for natural, low-calorie, clean-label alternatives. Regulatory approvals and government support have boosted adoption by major food and beverage brands. Technological advances in extraction and better-tasting steviol glycosides are overcoming the aftertaste barrier, broadening applications.
Challenges remain: heavy reliance on China for supply creates price volatility and geopolitical risks, while competition from other sweeteners intensifies. Yet, consolidation—such as Ingredion’s acquisition of PureCircle—shows a trend toward vertical integration and control of high-purity ingredients. Combined with innovation, this positions Stevia for sustained growth and a stronger role in the global food and beverage industry.
Global Market Sizing and Forecast Reconciliation
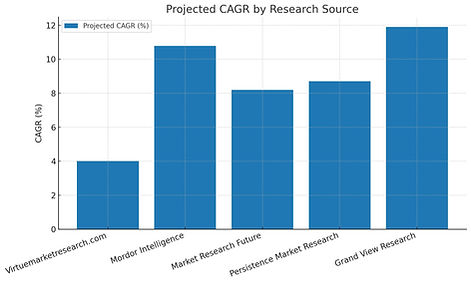
An initial review of the available market research data reveals a significant divergence in the valuation and growth forecasts for the global Stevia market. The reported figures for base year market size, forecast period, and projected CAGR vary considerably, presenting a confusing picture for anyone seeking a clear understanding of the market's scale.
The following table provides a direct comparison of these conflicting forecasts:
A superficial reading of market data—where base-year sizes differ by nearly USD 1 billion and CAGRs by over 7 percentage points—can lead to flawed conclusions. Expert analysis requires examining the causes of these discrepancies, not just the numbers.
The variance reflects the Stevia market’s fragmented identity. Reports cover different parts of the value chain: the Stevia Rebaudiana market, Stevia product market, and Stevia raw materials market. This shows there is no single definition of the "Stevia market," but rather an ecosystem spanning cultivation, raw leaf production, high-purity extraction, formulation, and end-use products. Forecasts differ because firms define the market boundaries differently.
This fragmentation is a strategic challenge. Companies offering integrated solutions—from sourcing to diverse product portfolios—are best positioned to capture share and provide stability.
Reconciling conflicting figures with prevailing drivers, the high-end CAGR projections are most credible. Strong demand for natural sweeteners, regulatory support, and advances in taste-enhancing technologies support the view that the global market will reach USD 0.9–1.1 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 8–10%.
Market Drivers
-
Sugar taxes & reformulation pressure: demonstrable sugar reductions in markets with levies (e.g., UK).
-
Clean-label, plant-based preference: stevia positions as a “from plant” alternative vs. artificial sweeteners.
-
Taste parity via tech: Reb M/D solutions reduce bitterness/lingering aftertaste, enabling higher replacement levels. Regulatory validation for bioconversion/fermentation widens use. (Ingredion, Cargill, European Food Safety Authority)
-
Sustainability claims: precision-fermented stevia can dramatically cut land/water vs. sugarcane. (Avansya LCA indicates ~81% lower GHG, 96% lower land use, 97% lower water vs. sugar.)
Headwinds
-
WHO 2023 guidance on NSS for weight control tempers “diet” positioning; brands pivot to sugar-reduction and taste outcomes. (World Health Organization)
-
Price/availability of high-purity glycosides (Reb M) & IP disputes (partially resolved in 2024) previously constrained adoption; approvals and legal clarity ease this. (Food Business News)
-
Regional regulatory nuances (e.g., specific product category restrictions in India such as cocoa/chocolate) require label vigilance. (Food Compliance International)
Market sizing & growth
-
Stevia ingredients (leaf extracts/derivatives):
2024–2025 market sizes between US$0.6–0.95B, with CAGR ~9–11% to 2031–2034. (Precision Business Insights, Claight) -
“All stevia” / “stevia leaf extract” verticals (selected segments):
Sub-segments like stevia powder and organic stevia show similar high-single-digit growth. (DataM Intelligence, Valuates Reports) -
Steviol glycosides (broader category):
US$5.31B (2024), projected US$7.15B by 2030, CAGR ~5.2%. This wider lens covers more applications and glycoside mixes. (Grand View Research) -
Outlook: Most forecasts converge on mid-to-high single-digit CAGR through 2030–2035; upside comes from next-gen Reb M penetration in beverages, dairy analogues, and bakery. (Future Market Insights)

Key Market Drivers: A Trifecta of Health, Regulation, and Technology
Stevia's growth is driven by three interconnected forces: rising health consciousness, supportive regulations, and continuous innovation.
The Health and Wellness Imperative
The global rise in obesity and diabetes has intensified demand for sugar alternatives. A 2024 IFIC study found 74% of U.S. consumers actively limit sugar. Consumers also prefer "clean-label," plant-based ingredients, boosting stevia’s appeal. This trend is creating a tiered market: conventional stevia holds 80.34% market share, but the organic segment is growing faster (CAGR of 10.2–11.43%), reflecting willingness to pay more for perceived health benefits.
The Power of Regulatory Support
Regulatory approvals—such as FDA GRAS status and EU authorization—have built trust in stevia. Sugar taxes in the U.K., France, and other regions push manufacturers to reformulate with non-caloric sweeteners. Industry pledges, like the UNESDA’s commitment to reduce sugar content by 10% by 2025, further drive adoption. Recent EU labeling updates to “steviol glycosides from stevia” improve transparency and reinforce its natural origin.
Technological Innovation as a Catalyst
Stevia’s historical aftertaste issues limited its use, with 35% of consumers dissatisfied. Innovation now focuses on superior-tasting glycosides like Reb M, which offers a sugar-like taste without bitterness. Advanced production methods—including bioconversion and fermentation—enable scalable, cost-effective production of these rare compounds. This shift supports new high-purity formulations and liquid formats, expanding stevia’s use in diverse applications.
Detailed Market Segmentation Analysis:
The Stevia market is best understood through its various segments, each with its own unique dynamics, growth rates, and drivers.
Segmentation by Application
The beverage industry represents the largest application segment for Stevia, capturing a market share of between 30.07% and 36.8%. This dominance is a direct result of global sugar-reduction initiatives and the soaring consumer demand for zero-calorie and diet beverages. The rapid growth of the liquid Stevia format is particularly tied to this segment, as it offers the precise sweetness control and complete dissolution required for beverages.
The food segment is also a major driver of demand and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 12.2%. This segment includes a wide range of products, from bakery and confectionery to dairy and frozen goods. Consumers are increasingly seeking healthier versions of these everyday items, creating a robust market for Stevia-based formulations.
Beyond the food and beverage industry, Stevia is finding its way into emerging applications. It is increasingly being used in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors, where its anti-diabetic, anti-hypertensive, and antioxidant properties make it a functional ingredient for sugar-free medicines and health supplements. The cosmetics and personal care sectors also represent a stable, growing opportunity, with Stevia being used in products such as creams, shampoos, and oral care formulations.
Beverages Dominate with 30–37%

Segmentation by Product Type and Form
The powdered form of Stevia currently holds a substantial market share, accounting for 63% to 95.34% of the market depending on the report. Its dominance is attributed to its high concentration, long shelf life, thermal stability, and versatility, which makes it well-suited for a wide range of manufacturing processes, including baking.
However, the liquid Stevia segment is the fastest-growing, with a projected CAGR of 12.58% through 2030.4 This growth is a direct result of technological advancements that have addressed previous challenges related to solubility and taste, making it ideal for the rapidly expanding zero-sugar beverage market.

Segmentation by Ingredient Type
The market is also segmented by its origin: conventional versus organic. Conventional Stevia holds a significant market share of 80.34%, primarily due to its cost advantages and established supply chains, which cater to price-sensitive manufacturers. Conversely, the organic Stevia segment is positioned for rapid growth, with a CAGR of 10.2% to 11.43%. This expansion is directly fueled by the premium consumer trend toward clean-label and chemical-free food products.

Segmentation by Glycoside (Reb A vs. Reb M)
The market for steviol glycosides is not homogenous. Reb A, or Rebaudioside A, is the most abundant and widely used glycoside. It is a cost-effective choice for manufacturers due to its abundance and established production methods.
In contrast, Reb M, or Rebaudioside M, has emerged as a premium solution. It provides a clean, sugar-like taste making it highly desirable for premium applications. Reb M is significantly more expensive than Reb A because it is found in very low quantities in the Stevia plant and requires complex extraction and purification processes. However, its superior taste profile justifies its higher price point, as evidenced by the Reb M market itself, which reached 73.38 million USD in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.92% through 2031. This segmentation highlights a clear market dynamic: a mature, price-sensitive market for commodity-grade steviol glycosides and a fast-growing, high-margin market for advanced, premium solutions.

Regional Market Dynamics: A Global Tapestry
The Stevia market exhibits distinct regional dynamics, with each major geography playing a unique role in the global ecosystem.
Asia-Pacific: The Dual-Role Powerhouse
The Asia-Pacific region is the largest and one of the fastest-growing markets for Stevia, commanding a market share ranging from 31.43% to 48.8%.4 The region's growth is fueled by increasing health consciousness, a rising prevalence of obesity and diabetes, and robust government support for natural sweetener adoption. China stands as the world's leading producer and cultivator of Stevia, benefiting from large-scale production facilities, lower labor costs, and efficient supply chains.3 Simultaneously, countries like Japan are major consumers, where Stevia has enjoyed longstanding acceptance, and India is experiencing a particularly rapid expansion with a projected CAGR of 8.9%.
However, this regional dominance presents a strategic risk. The industry's over-reliance on a single production hub, primarily China, creates a significant vulnerability to supply chain disruptions stemming from agricultural factors, unpredictable weather, and geopolitical events. This risk is underscored by instances such as U.S. Customs seizing Chinese Stevia extracts over forced labor concerns. The industry is actively responding to this concentration risk by promoting the "localization of production and sourcing" in other APAC regions, supported by government policies and R&D funding. This strategic shift, while potentially raising short-term costs, is a fundamental evolution aimed at building a more resilient and geographically diversified supply chain.
Asia-Pacific leads the Stevia market with 31.4–48.8% share,. China dominates production due to scale and cost advantages, while Japan is a key consumer and India shows rapid growth (CAGR 8.9%).
North America: A Mature and Conscious Market
North America is a leading market for Stevia, driven by a strong consumer preference for healthier, low-calorie, and clean-label sweeteners. The region holds a significant market share, with reports citing figures of 40% and 36%. This dominance is rooted in a mature market with a high degree of health awareness, where consumers are actively seeking alternatives to traditional sugar to support dietary goals and manage conditions like diabetes and obesity.
North America holds 36–40% of the Stevia market, driven by strong demand for healthy, low-calorie, clean-label sweeteners, supported by high health awareness.
Europe: Regulatory Momentum Fuels Rapid Growth
The European Stevia market is distinguished by its rapid growth, with a projected CAGR of 12.8%.14 This acceleration is a direct consequence of a favorable regulatory environment. The approval of Stevia extracts in the European Union in 2011, followed by a series of amendments that expanded its permitted uses and forms, unlocked significant growth potential.10 Consumer awareness is also on the rise, and recent labeling changes are expected to further boost adoption by clarifying the product's natural origin.10 The EU's push for sugar reduction, reinforced by a "Code of Conduct for responsible food business," continues to foster demand and innovation.
The European Stevia market is growing rapidly at a 12.8% CAGR, driven by favorable regulations, rising consumer awareness, clearer labeling, and the EU’s sugar-reduction policies.
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Consolidation
The global Stevia market is characterized by a "medium" level of concentration, with a handful of major players holding significant market shares. The largest of these is PureCircle (an Ingredion subsidiary), which holds an estimated 25% share of the market. Other key players include Cargill, Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), and Tate & Lyle.
A pivotal event that reshaped the competitive landscape was Ingredion's 2020 acquisition of a 75% controlling stake in PureCircle. This strategic maneuver offers a crucial look into the market's maturation. Ingredion, a global provider of ingredient solutions, sought to fortify its position in the rapidly growing sugar reduction and specialty sweetener market. PureCircle, a pioneer in Stevia innovation with a vast knowledge base, was simultaneously facing significant financial challenges. The acquisition was a symbiotic union that rescued PureCircle's technological and vertical integration capabilities while granting Ingredion immediate and profound leadership in the Stevia market.
This consolidation signals a strategic shift within the industry. It moves Stevia from a niche ingredient to a core component of a major food ingredient company's portfolio. The acquisition also enabled Ingredion to leverage PureCircle's technological expertise to offer advanced solutions like Reb M from three different production technologies: stevia leaf extract, bioconversion, and fermentation. This integrated approach allows Ingredion to provide a comprehensive, high-purity sweetener portfolio, addressing diverse customer needs and reinforcing its market leadership.

Economic Insights and Market Challenges
The robust growth of the Stevia market does not come without its economic and operational challenges.
Supply Chain and Price Volatility
The market is susceptible to price volatility due to a dependence on agricultural factors and a concentrated production base. Stevia prices are influenced by unpredictable weather and geopolitical events, which can disrupt supply chains and complicate price forecasts.
A significant portion of the world's Stevia cultivation and processing is concentrated in a few key regions, particularly China.3 While this concentration has historically led to cost efficiencies, it also increases risks from localized disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
For example, regional price analysis shows a variance, with China's Stevia prices at 77300 USD/MT in June 2025, compared to 87117 USD/MT in the USA during the same period, reflecting the influence of local supply chains, freight costs, and currency fluctuations.
The Aftertaste Barrier Revisited
Despite progress, lingering aftertaste limits consumer acceptance, particularly in regions with strong flavor preferences. Effectively masking it and creating sugar-like formulations is crucial for expanding into new food and beverage categories.
Competition from a Crowded Market
Stevia faces intense competition from natural sweeteners like monk fruit and erythritol, and FDA-approved artificial options such as sucralose (Splenda), saccharin (Sweet'N Low), and aspartame (Equal). This crowded market demands constant innovation in taste, functionality, and cost-effectiveness to sustain growth.

Strategic Outlook and Recommendations
The future of the Stevia market will be defined by its ability to navigate a complex environment of rapid growth, technological disruption, and operational risk.
Forward-Looking Analysis
The market is clearly moving toward premiumization and technological sophistication. The traditional view of Stevia as a single, homogenous commodity is giving way to a more nuanced understanding of a market driven by specialized, high-purity steviol glycosides.
The aftertaste issue, once a major restraint, has been transformed into a powerful catalyst for innovation, pushing companies to invest in R&D and advanced production technologies like bioconversion and fermentation.
The strategic acquisition of key innovators by larger ingredient companies signals a consolidation phase that will likely lead to more integrated, resilient, and comprehensive market offerings.
Continued R&D in taste improvement, cost reduction, and sustainable sourcing will enhance adoption.
Asia-Pacific will remain the production hub, while North America and Europe drive consumption. Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa offer untapped potential.
Sugar taxes and clean-label regulations will accelerate stevia integration in F&B portfolios.
Strategic Recommendations
For Investors: The most significant opportunities lie in companies that have a vertically integrated supply chain and a robust R&D pipeline for developing advanced steviol glycosides like Reb M. These companies are best positioned to capture high-margin growth and provide stable, reliable supply to global manufacturers. A focus on firms that are diversifying their production base to mitigate geopolitical risk is also advisable.
For Manufacturers: To remain competitive, manufacturers should prioritize collaborative R&D with sweetener suppliers to develop custom formulations that specifically address the taste, solubility, and functionality challenges for their product categories. This requires a move beyond off-the-shelf ingredients toward specialized, co-created solutions. Diversifying sourcing away from concentrated regions can also provide long-term supply chain resilience.
For Marketers: The focus should be on building consumer trust through clear, transparent, and accurate labeling that highlights Stevia's natural, plant-based origin. Leveraging recent regulatory changes, such as the new EU labeling for "Steviol glycosides from stevia," can be a powerful tool to educate consumers and reinforce the product's clean-label credentials.

Technological Innovations and New Production Methods:
Fermentation and Bioconversion: A major investment theme is the shift from traditional agricultural extraction to innovative production methods like bioconversion and fermentation. These technologies are producing higher-purity steviol glycosides (like Reb M and Reb D), which have a more sugar-like taste and minimal aftertaste.
Sustainability and Efficiency:
These new production methods offer significant sustainability advantages. They require less land and water than traditional agriculture and result in a dramatically lower carbon footprint. Companies that are vertically integrated or investing in these technologies are gaining a competitive edge.
Strategic and Operational Opportunities:
Vertical Integration: Companies that control their supply chain, from farming to extraction and refinement, are better positioned to ensure a stable, high-quality, and traceable supply. This is a critical factor for building trust with large food and beverage manufacturers.
R&D and Product Blending:
Continued research and development is crucial for creating new stevia blends and formulations that can mimic the taste, mouthfeel, and functionality of sugar. Investing in firms with a strong R&D pipeline that focuses on taste-masking and solubility is a key opportunity.
Geographic Diversification: While Asia-Pacific, particularly China, remains a dominant producer, there is a growing trend towards localized production. Investments in regional hubs and local farming initiatives can reduce supply chain risks and cater to local market demands.






